If your home uses a boiler for heat, water pressure plays a critical role in both performance and safety. One of the most common questions homeowners ask is:
“What should my boiler pressure be?”
The answer is more specific than most people realize — and getting it wrong can lead to system failure, leaks, or costly repairs.
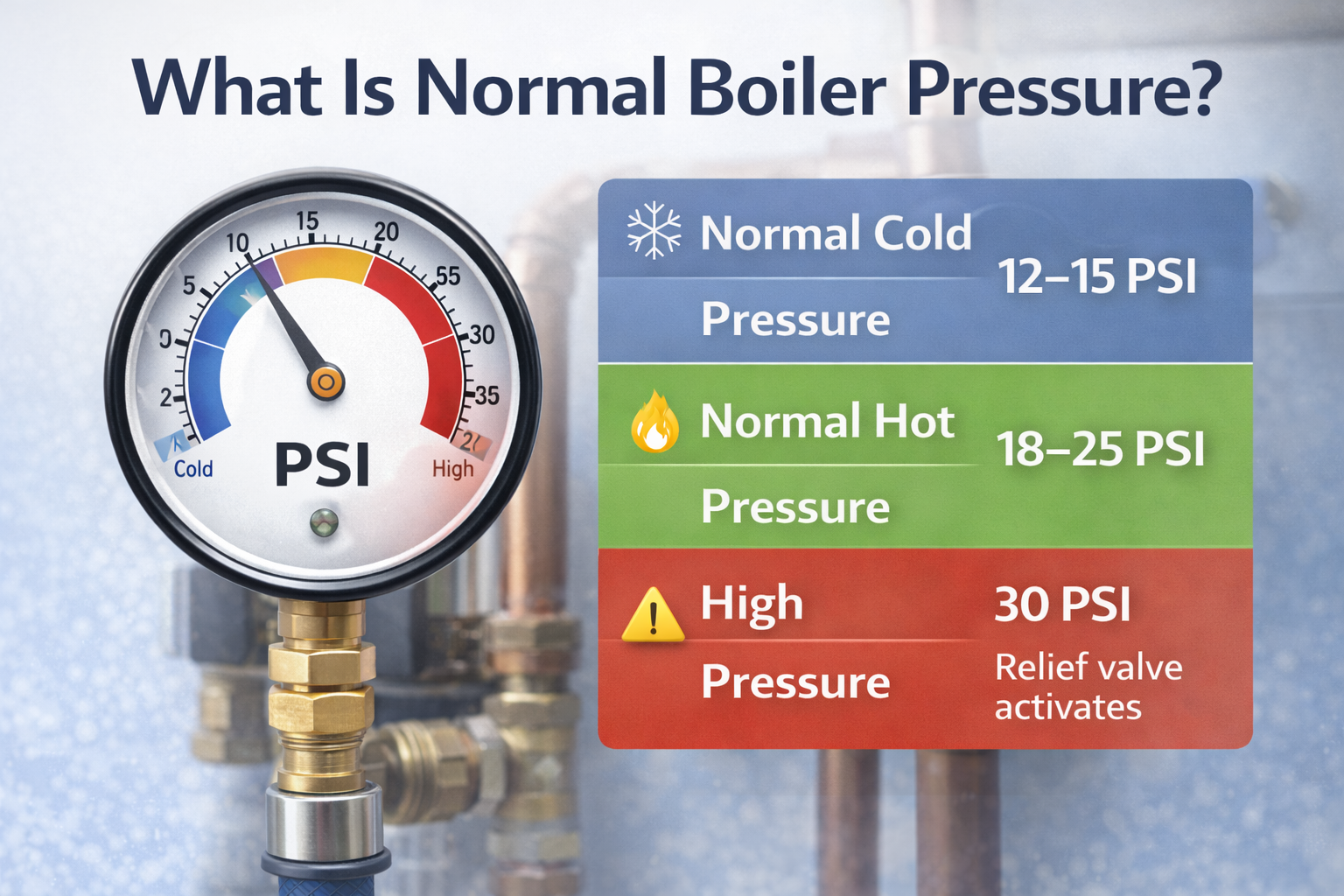
Normal Boiler Pressure (Cold vs. Hot)
For most residential boiler systems:
Normal cold boiler pressure: 12–15 PSI
Normal operating (hot) pressure: 18–25 PSI
Relief valve activates at: 30 PSI
These ranges apply to the majority of hydronic (hot water) boilers found in older and newer homes throughout Pennsylvania and New Jersey.
📌 Key fact:
Boiler pressure is designed around the height of your home. A two-story house typically needs 12 PSI just to move water to the highest radiator or baseboard.
Why Boiler Pressure Changes When Heating
When water heats up, it expands. That expansion increases pressure inside the system.
This is why modern boilers rely on an expansion tank to absorb extra pressure. Without a properly working expansion tank, pressure can rise rapidly and trigger leaks or relief valve discharge.
What Causes High Boiler Pressure?
High boiler pressure is not normal and should never be ignored. Common causes include:
Failed or waterlogged expansion tank
Automatic feed valve stuck open
Overfilled system
Improper system purging
Closed isolation valves near the expansion tank
⚠️ Important:
If your boiler pressure regularly climbs above 25 PSI, it’s a warning sign — even if the system still seems to work.
What Causes Low Boiler Pressure?
Low pressure can prevent heat from reaching parts of the home. Common causes include:
Small system leaks
Air trapped in radiators or baseboards
Recently bled radiators without refilling
Failing feed valve
Most boilers will shut down automatically if pressure drops too low to protect the system.
Can High Boiler Pressure Damage the System?
Yes — and often quietly.
Sustained high pressure can:
Shorten circulator pump life
Cause relief valves to fail prematurely
Stress heat exchangers
Lead to hidden leaks inside walls or ceilings
Many homeowners only notice a problem after water damage appears.
Where to Check Boiler Pressure
Most boilers have a pressure gauge mounted on the front or near the piping. If the gauge is unreadable, inaccurate, or missing, pressure issues can go unnoticed for years.
📌 Pro tip:
Pressure should be checked when the system is cold for the most accurate baseline reading.
When to Call a Professional
You should have your boiler checked if:
Pressure rises close to 30 PSI
The relief valve leaks or drips
Pressure frequently drops below 12 PSI
Heat is uneven throughout the home
Boiler pressure issues are often linked to components that require professional testing — not guesswork.
Final Thoughts
Boiler pressure is one of the most important — and misunderstood — parts of a heating system. Knowing the correct PSI ranges can help prevent breakdowns, extend system life, and protect your home from water damage.
If your boiler pressure doesn’t stay within normal limits, it’s best to address it before the heating season puts added stress on the system.